IoT Architecture
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network in which various objects are interlinked, encompassing a dual significance. On one hand, it underscores that at its core, the IoT functions within an internet framework. Essentially, the IoT is a technological advancement built upon the foundations of internet-based technologies. On the other hand, it signifies that the entities linked to the internet extend beyond mere computers and mobile phones; they encompass an array of items in our vicinity, including air conditioners and refrigerators. The primary objective of IoT technology is to facilitate the seamless integration of a wide spectrum of objects into the internet realm.
Ever since the inception of the Internet, human beings have drawn closer together. The Internet of Things (IoT) establishes connections across a myriad of entities. In the age of information proliferation, what is visible on the web can be aptly characterized as data. Essentially, the IoT functions as a technology that serves data. Constructing such a realm of IoT necessitates devices in connection to possess an intelligence that comprehends our requirements, thereby furnishing us with more sophisticated services.
The architecture of the IoT comprises four fundamental tiers: application, platform, network, and sensing.
The sensing tier represents the stratum of objects, housing a diverse array of sensors, chipsets, and modules. This level is tasked with gathering data, processing signals, and utilizing a communication module to interact with the platform tier, facilitating the transmission of data.
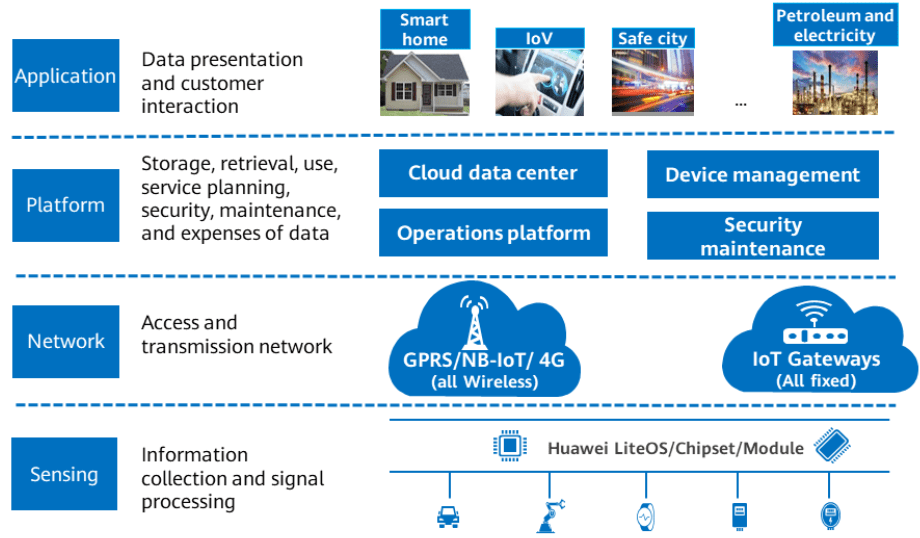
Image Source = HCIA IoT
Tingkat jaringan berfungsi sebagai saluran komunikasi, menjembatani kesenjangan antara tingkat penginderaan dan platform. Transmisi data ke lapisan platform dapat dilakukan melalui berbagai cara, termasuk jaringan nirkabel seperti GPRS, NB-IoT, atau 4G, serta akses kabel melalui gateway.
Lapisan platform memegang tugas penyimpanan, pemanfaatan, dan pemeliharaan data. Data yang diperoleh dapat digunakan untuk beragam tugas, termasuk pemrosesan data dan operasi lainnya. Sebaliknya, lapisan aplikasi berpusat pada pelanggan dan dipercayakan dengan tugas menyajikan akumulasi data dengan cara yang disesuaikan.
IoT Applications
Smart City Solution
The smart city solution brings forth its benefits through three key dimensions: it minimizes the complexity of developing IoT applications, eases the challenges faced by developers, and accelerates the incubation period for the complete IoT city ecosystem. This approach expedites the realization of a smart city ecosystem. The platform effectively consolidates data from various urban facets, delivering enhanced convenience in comprehensive city management services. With regards to devices and networks, this solution tailors itself to the devices and standards in use, establishing a standardized management framework for city administrators, thereby circumventing fragmented integration of IoT applications into the platform.
Smart Campus Solution
The solution’s comprehensive structure is segmented into three core components. The initial tier, the sensing layer, encompasses an array of intelligent devices situated within smart campuses. These devices facilitate data transmission towards the management platform. Following this, the platform undertakes data processing and analysis, subsequently uploading the information to the cloud to cater to user services.
Regarding visitor management, the process involves advance reservation by the visitor. Once confirmed, the visitor receives an SMS containing a verification code. Displaying this code to a security guard grants the visitor a temporary pass for campus access, resulting in substantial time savings.
Smart Grid Solution
The implementation of smart metering supersedes manual metering procedures, resulting in enhanced precision, efficiency, and reduced costs in the metering process. Furthermore, the accurate data garnered through smart metering facilitates the assessment of power consumption levels, both on a per-area and per-dwelling basis. This data serves as a foundation for strategic power generation allocation, detailed user consumption analysis, and the provision of energy-efficient solutions.
In the quest to establish seamlessly interconnected grids, the solution’s scope extends beyond mere power transmission to encompass the flow of data. A truly interconnected grid implies centralized management of all devices employed in the power transportation workflow, with the generated data being transmitted to the cloud. This cloud-based system orchestrates the comprehensive operation of the entire power network. The integration of novel technologies across production, management, and marketing of power grids further contributes to the development of fully connected power grids. These grids interlink numerous devices, boasting attributes like heightened security, minimal latency, extensive coverage, and energy efficiency.
Internet of Vehicle (IoV) Solution
The technology addressing the aforementioned challenges is known as the Internet of Vehicles (IoV). IoV harnesses in-vehicle devices and wireless communication technologies to leverage the complete spectrum of vehicle information within an information network platform, enabling diverse functionalities. IoV is an integral facet of the broader Internet of Things (IoT). Initially, it incorporates in-vehicle devices situated within the sensing layer. Moreover, it employs wireless communication technologies to transmit vehicle data to the platform for comprehensive analysis. This platform subsequently furnishes the data to applications for further analysis and functional execution.
Furthermore, the IoV is poised to evolve with the integration of edge computing capabilities in the coming years. Vehicles within the IoV ecosystem will exhibit intelligence, allowing them to autonomously regulate distances between themselves and other vehicles, thereby mitigating accidents—irrespective of the intelligence of other vehicles. Vehicles operating within the IoV framework will possess the capability to engage in inter-vehicle communication, subsequently amplifying traffic efficiency.
Industrial IoT Solution
What steps can be taken to attain complete connectivity? The solution lies in harnessing a range of emerging ICT technologies. The initial requirement involves imbuing intelligence within devices situated at the sensing layer. By facilitating the connection and communication between devices employing diverse communication protocols, collaborative functionality can be established among them.
Read more about IoT :
https://miqbal.staff.telkomuniversity.ac.id/apa-itu-internet-of-things/
And you can learn about IoT technical, please use this tag “IoT” blog
https://miqbal.staff.telkomuniversity.ac.id/topics/iot/
References :
- HCIA Internet of Things : https://ilearningx.huawei.com/portal/
- https://telkomuniversity.ac.id/
- https://www.particle.io/?utm_source=adwords&utm_medium=cpc&utm_campaign=1-SL-IoT-General&utm_content=contact_sales&gad=1&gclid=CjwKCAjwxaanBhBQEiwA84TVXAvMwzv02SSitwiJLkkmIuOzoza4jSWGZIX0RoMse_LDLnyj2O7oqhoCc-0QAvD_BwE
- https://apps.boschrexroth.com/microsites/ctrlx-automation/en/portfolio/ctrlx-iot/?utm_term=technologies%20iot&utm_campaign=AE+-+ctrlX+AUTOMATION+%26+Other+ctrlX+Products+-+Paid+Search+2023&utm_source=adwords&utm_medium=ppc&hsa_acc=3697502243&hsa_cam=20220459761&hsa_grp=150553422620&hsa_ad=660467976911&hsa_src=g&hsa_tgt=kwd-319434163894&hsa_kw=technologies%20iot&hsa_mt=p&hsa_net=adwords&hsa_ver=3&gclid=CjwKCAjwxaanBhBQEiwA84TVXDj5gLHl0CBEw_byYYaaPAuQfAGt_LkUwJZE8hoUvQK5A-gdI2qyWBoChfQQAvD_BwE
- https://www.statista.com/topics/5236/internet-of-things-iot-in-the-us/#editorsPicks