2.1 Footprinting Concepts
What is Footprinting?
- Footprinting is the process of collecting as much information as possible about a target network, for identifying various ways to intrude into an organization’s network system.
- Footprinting is the first step of any attack on information systems; attacker gathers publicly available sensitive information, using which he/she performs social engineering, system and network attacks, etc. that leads to huge financial loss and loss of business reputation.
- Know Security Posture: Footprinting allows attackers to know the external security posture of the target organization.
- Reduce Focus Area: It reduces attacker’s focus area to specific range of IP address, networks, domain names, remote access, etc.
- Identify Vulnerabilities: It allows attacker to identify vulnerabilities in the target systems in order to select appropriate exploits.
- Draw Network Map: It allows attackers to draw a map or outline the target organization’s network infrastructure to know about the actual environment that they are going to break.
Objectives of Footprinting
- Collect Network Information:
- Domain name
- Internal domain names
- Network blocks
- IP addresses of the reachable systems
- Rogue websites/private websites
- TCP and UDP services running
- Access control Mechanisms and ACL’s
- Networking protocols
- VPN Points
- IDSes running
- Analog/digital telephone numbers
- Authentication mechanisms
- System Enumeration
- Collect System Information:
- User and group names
- System banners
- Routing tables
- SNMP information
- System architecture
- Remote system type
- System names
- Passwords
- Collect Organization’s Information:
- Employee details
- Organization’s website
- Company directory
- Location details
- Address and phone numbers
- Comments in HTML source code
- Security policies implemented
- Web server links relevant to the organization
- Background of the organization
- News articles
- Press releases
2.2 Footprinting Methodology
2.2.1 Footprinting through Search Engines
Footprinting through Search Engines
- Attackers use search engines to extract information about a target such as technology platforms, employee details, login pages, intranet portals, etc. which helps in performing social engineering and other types of advanced system attacks.
- Search engine caches and internet archives may also provide sensitive information that has been removed from the World Wide Web (WWW).
Finding Company’s Public and Restricted Websites
- Search for the target company’s external URL in a search engine such as Google, Bing, etc.
- Restricted URLs provide an insight into different departments and business units in an organization.
- You may find a company’s restricted URLs by trial and error method or using a service such as http://www.netcraft.com
Determining the Operating System
- Use the Netcraft tool to determine the OSes in use by the target organization.
- Use SHODAN search engine that lets you find specific computers (routers, servers, etc.) using a variety of filters.
或是Censys, https://www.censys.io/
Collect Location Information
- Use Google Earth tool to get the physical location of the target.
- Tools for finding the geographical location:
- Google Earth
- Google Maps
- Wikimapia
- National Geographic Maps
- Yahoo Maps
- Bing Maps
People Search: Social Networking Sites/People Search Services
- Social networking sites are the great source of personal and organizational information.
- Information about an individual can be found at various people search websites.
- The people search returns the following information about a person or organization:
- Residential addresses and email addresses
- Contact numbers and date of birth
- Photos and social networking profiles
- Blog URLs
- Satellite pictures of private residencies
- Upcoming projects and operating environment
People Search Online Services
Gather Information from Financial Services
- Financial services provides a useful information about the target company such as the market value of a company’s shares, company profile, competitor details, etc.
Footprinting through Job Sites
- You can gather company’s infrastructure details job postings.
- Look for these:
- Job requirements
- Employee’s profile
- Hardware information
- Software information
Monitorming Target Using Alerts
- Alerts are the content monitoring services that provide up-to-date information based on your preference usually via email or SMS in an automated manner.
- Examples of Alert Services:
- Google Alerts – http://www.google.com/alerts
- Yahoo! Alerts – http://alerts.yahoo.com
- Twitter Alerts – https://twitter.com/alerts
- Giga Alert – http://www.gigaalert.com
Information Gathering Using Groups, Forums, and Blogs
- Groups, forums, and blogs provide sensitive information about a target such as public network information, system information, personal information, etc.
- Register with fake profiles in Google groups, Yahoo groups, etc. and try to join the target organization’s employee groups where they share personal and company information.
- Search for information by Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN), IP addresses, and usernames in groups, forums, and blogs.
2.2.2 Footprinting Using Advanced Google Hacking Techniques
Footprint Using Advanced Google Hacking Techniques
- Query String: Google hacking refers to creating complex search queries in order to extract sensitive or hidden information.
- Vulnerable Targets: It helps attackers to find vulnerable targets.
- Google Operators: It uses advanced Google search operators to locate specific strings of text within the search results.
Google Advance Search Operators (重要)
- Google supports several advanced operators that help in modifying the search:
- [cache:] Displays the web pages stored in the Google cache
- [link:] Lists web pages that have links to the specified web page
- [related:] Lists web pages that are similar to a specified web page
- [info:] Presents some information that Google has about a particular web page
- [site:] Restricts the results to those websites in the given domain
- [allintitile:] Restricts the results to those websites with all of the search keywords in the title
- [intitle:] Restricts the results to documents containing the search keyword in the title
- [allinurl:] Restricts the results to those with all of the search keywords in the URL
- [inurl:] Restricts the results to documents containing the search keyword in the URL
Google Hacking Databases
- Google Hacking Database (GHDB): http://www.hackersforcharity.org
- Google Dorks: http://www.exploit-db.com
Information Gathering Using Google Advanced Search
- Use Google Advanced Search option to find sites that may link back to the target company’s website.
- This may extract information such as partners, vendors, clients, and other affiliations for target website.
- With Google Advanced Search option, you can search web more precisely and accurately
2.2.3 Footprinting through Social Networking Sites
Collect Information through Social Engineering on Social Networking Sites
- Attackers use social engineering trick to gather sensitive information from social networking websites such as Facebook, MySpace, LinkedIn, Twitter, Pinterest, Google+, etc.
- Attackers create a fake profile on social networking sites and then use the false identity to lure the employees to give up their sensitive information.fake id generator
- Employees may post personal information such as date of birth, educational and employment backgrounds, spouses names, etc. and information about their company such as potential clients and business partners, trade secrets of business, websites, company’s upcoming news, mergers, acquisitions, etc.
- Attackers collect information about employee’s interests by tracking their groups and then trick the employee to reveal more information.
Information Available on Social Networking Sites
| What Attacker Gets | What Users Do | What Organizations Do | What Attacker Gets |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact info, location, etc. | Maintain profile | User surveys | Business strategies |
| Friends list, friends info, etc. | Connect to friends, chatting | Promote products | Product profile |
| Identify of a family members | Share photos and videos | User support | Social engineering |
| Interests | Play games, join groups | Recruitment | Platform/technology information |
| Activities | Creates events | Background check to hire employees | Type of business |
2.2.4 Website Footprinting
Website Footprinting
- Website Footprinting referes to monitoring and analyzing the target organization’s website for information.
- Browsing the target website may provide:
- Software used and its version
- Operating system used
- Sub-directories and parameters
- Filename, path, database field name, or query
- Scripting platform
- Contact details and CMS details
- Use Burp Suite, Zaproxy, Paros Proxy, Website Informer, Firebug, etc. to view headers that provide:
- Connection status and content-type
- Accept-Ranges
- Last-Modified information
- X-Powered-By information
- Web server in use and its version
- Examining HTML source provide:
- Comments in the source code
- Contact details of web developer or admin
- File system structure
- Script type
- Examining cookies may provide:
- Software in use and its behavior
- Scripting platforms used
Website Footprinting using Web Spiders
- Web spiders perform automated searches on the target websites and collect specified information such as employee names, email addresses, etc.
- Attackers use the collected information to perform further footprinting and social engineering attacks.
- GSA Email Spider: http://email.spider.gsa-online.de
- Web Data Extractor: http://webextractor.com
Mirroring Entire Website
- Mirroring an entire website onto the local system enables an attacker to browse website offline; it also assists in finding directory structure and other valuable information from the mirrored copy without multiple requests to web server.
- Web mirroring tools allow you to download a website to a local directory, building recursively all directories, HTML, images, flash, videos, and other files from the server to your computer.
- wget -m
- HTTrack Web Site Copier: http://www.httrack.com
- SurfOffline: http://www.surfoffline.com
Website Mirroring Tools
Extract Website Information from http://www.archive.org (重要)
- Internet Archive’s Wayback Machine allows you to visit archived versions of websites.
google cache:
Monitoring Web Updates Using Website-Watcher
- Website-Watcher automatically checks web pages for updates and changes.
Web Updates Monitoring Tools
2.2.5 Email Footprinting
Tracking Email Communications
- Email tracking is used to monitor the delivery of emails to an intended recipient.
- Attackers track emails to gather information about a target recipient in order to perform social engineering and other attacks.
- Get recipient’s system IP address
- Geolocation of the recipient
- When the email was received and read
- Whether or not the recipient visited any links sent to them
- Get recipient’s browser and operating system information
- Time spent on reading the emails
Collecting Information from Email Header

Email Tracking Tools
- eMailTrackerPro: http://www.emailtrackerpro.com
- PoliteMail: http://www.politemail.com
- Email Lookup – Free Email Tracker: http://www.ipaddresslocation.org
2.2.6 Competitive Intelligence
Competitive Intelligence Gathering
- Competitive intelligence gathering is the process of identifying, gathering, analyzing, verifying, and using information about your competitors from resources such as the Internet.
- Competitive intelligence is non-interfering and subtle in nature.
- Sources of Competitive Intelligence:
- Company websites and employment ads
- Search engines, Internet, and online DB
- Press releases and annual reports
- Trade journals, conferences, and newspaper
- Patent and trademarks
- Social engineering employees
- Product catalogues and retail outlets
- Analyst and regulatory reports
- Customer and vendor interviews
- Agents, distributors, and suppliers
Competitive Intelligence – When Did this Company Begin? How Did it Develop?
- When did it begin?
- EDGAR Database: http://www.sec.gov/edgar.shtml
- How did it develop?
- Hoovers: http://www.hoovers.com/about-us.html
- Where is it located?
- LexisNexis: http://www.lexisnexis.com
- Who leads it?
- Business Wire: http://www.businesswire.com
Competitive Intelligence – What Are the Company’s Plans?
Competitive Intelligence – What Expert Opinions Say About the Company
Monitoring Website Traffic of Target Company
- Attacker uses website traffic monitoring tools such as web-stat, Alexa, Monitis, etc. to collect the information about target company:
- Total visitors
- Page views
- Bounce rate
- Live visitors map
- Site ranking
- Traffic monitoring helps to collect information about the target’s customer base which help attackers to disguise as a customer and launch social engineering attacks on the target.
Tracking Online Reputation of the Target
- Online Reputation Management (ORM) is a process of monitoring a company’s reputation on Internet and taking certain measures to minimize the negative search results/reviews and thereby improve its brand reputation.
- An attacker makes use of ORM tracking tools to:
- Track company’s online reputation
- Collect company’s search engine ranking information
- Obtain email notifications when a company is mentioned online
- Track conversations
- Obtain social news about the target organization
2.2.7 WHOIS Footprinting
WHOIS Lookup
- WHOIS databases are maintained by Regional Internet Registries and contain the personal information of domain owners.
- WHOIS query returns:
- Domain name details
- Contact details of domain owner
- Domain name servers
- NetRange
- When a domain has been created
- Expiry records
- Records last updated
- Information obtained from WHOIS database assists an attacker to:
- Gather personal information that assists to perform social engineering
- Regional Internet Registries (RIRs):
- AFRINIC (African Network Information Center)
- ARIN (American Registry for Internet Numbers)
- APNIC (Asia Pacific Network Information Center)
- RIPE (Reseaux IP Europeens Network Coordination Centre)
- LACNIC (Latin American and Caribbean Network Information Center)
2.2.8 DNS Footprinting
Extracting DNS Information (重要)
- Attacker can gather DNS information to determine key hosts in the network and can perform social engineering attacks.
- DNS records provide important information about location and type of servers.
- DNS Interrogation Tools:
- Name -> IP
- IP -> Name
- Service -> Name
| Record | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Points to a host’s IP address |
| MX | Points to domain’s mail server |
| NS | Points to host’s name server |
| CNAME | Canonical naming allows aliases to a host |
| SDA | Indicate authority for domain |
| SRV | Service records |
| PTR | Maps IP address to a hostname |
| RP | Responsible person |
| HINFO | Host information record includes CPU type and OS |
| TXT | Unstructured text records |
- Linux
hostcommand - GET dns.google.com
- dnsdumpster
2.2.9 Network Footprinting
Locate the Network Range
- Network range information assists attackers to create a map of the target network.
- Find the range of IP addresses using ARIN whois database search tool.
- You can find the range of IP addresses and the subnet mask used by the target organization from Regional Internet Registry (RIR).
Traceroute (重要)
- Traceroute programs work on the concept of ICMP protocol and use the TTL field in the header of ICMP packets to discover the rotuers on the path to a target host.
- Manual traceroute: ping -i 1
- UDP 33434-33534 Random
- ICMP type3: Destination Unreachable
- ICMP type11: Time Exceeded
Traceroute Analysis
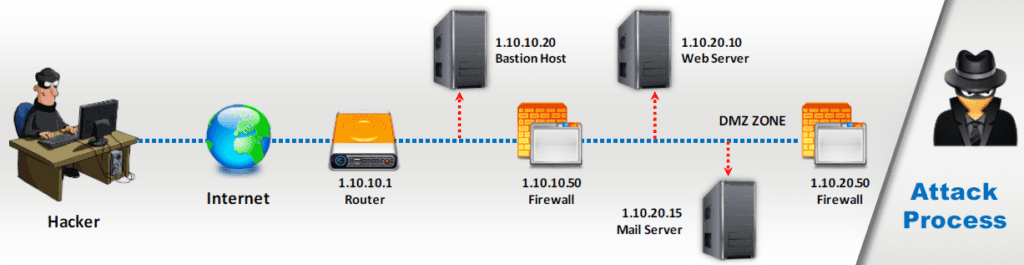
- Attackers conduct traceroute to extract information about: network topology, trusted routers, and firewall locations.
- For example: after running several traceroutes, an attacker might obtain the following information:
- traceroute 1.10.10.20, second to last hop is 1.10.10.1
- traceroute 1.10.10.20, third to last hop is 1.10.10.1
- traceroute 1.10.20.10, second to last hop is 1.10.10.50
- traceroute 1.10.20.15, third to last hop is 1.10.10.1
- traceroute 1.10.20.15, second to last hop is 1.10.10.50
- By putting this information together, attackers can draw the network diagram.
2.2.10 Footprinting through Social Engineering
Footprinting through Social Engineering
- Social engineering is an art of exploiting human behavior to extract confidential information.
- Social engineers depend on the fact that people are unaware of their valuable information and are careless about protecting it.
- Social engineers attempt to gather:
- Credit card details and social security number
- User names and passwords
- Security products in use
- Operating systems and software versions
- Network layout information
- IP addresses and names of servers
- Social engineering techniques:
- Eavesdropping
- Shoulder surfing
- Dumpster diving
- Impersonation on social networking sites
Collect Information Using Eavesdropping, Shoulder Surfing, and Dumpster Diving
- Eavesdropping:
- Eavesdropping is unauthorized listening of conversations or reading of messages.
- It is interception of any form of communication such as audio, video, or written.
- Shoulder Surfing:
- Shoulder surfing is a technique, where attackers secretly observes the target to gain critical information
- Attackers gather information such as passwords, personal identification number, account numbers, credit card information, etc.
- Dumpster Diving:
- Dumpster diving is looking for treasure in someone else’s trash.
- It involves collection of phone bills, contact information, financial information, operations related information, etc. from the target company’s trash bins, printer trash bins, user desk for sticky notes, etc.
2.3 Footprinting Tools
Footprinting Tool: Maltego (重要)
- Maltego is a program that can be used to determine the relationships and real world links between people, groups of people (social networks), companies, organizations, websites, Internet infrastructure, phrases, documents, and files.
Footprinting Tool: Recon-ng
- Recon-ng is a Web Reconnaissance framework with independent modules, database interaction, built in convenience functions, interactive help, and command completion, that provides an environment in which open source web-based reconnaissance can be conducted.
Footprinting Tool: FOCA (重要)
- FOCA(Fingerprinting Organizations with Collected Archives) is a tool used mainly to find metadata and hidden information in the documents its scans.
- Using FOCA, it is possible to undertake multiple attacks and analysis techniques such as metadata extraction, network analysis, DNS snooping, proxies search, fingerprinting, open directories search, etc.
2.4 Footprinting Countermeasures
Footprinting Countermeasures
- Restrict the employees to access social networking sites from organization’s network
- Configure web servers to avoid information leakage
- Educate employees to use pseudonyms on blogs, groups, and forums
- Do not reveal critical information in press releases, annual reports, product catalogues, etc.
- Limit the amount of information that you are publishing on the website/Internet
- Use footprinting techniques to discover and remove any sensitive information publicly available
- Prevent search engines from caching a web page and use anonymous registration services
- Enforce security policies to regulate the information that employees can reveal to third parties
- Set apart internal and external DNS or use split DNS, and restrict zone transfer to authorized servers
- Disable directory listings in the web servers
- Educate employees about various social engineering tricks and risks
- Opt for privacy services on Whois Lookup database
- Avoid domain-level cross-linking for the critical assets
- Encrypt and password protect sensitive information
2.5 Footprinting Penetration Testing
Footprinting Pen Testing
- Footprinting pen testing is used to determine organization’s publicly available information.
- The tester attempts to gather as much information as possible about the target organization from the Internet and other publicly accessible sources.
- Footprinting pen testing helps organization to:
- Prevent DNS record retrieval from publically available servers
- Prevent information leakage
- Prevent social engineering attempts
- Get proper authorization and define the scope of the assessment.
- Foorprint search engines such as Google, Yahoo!Search, Ask, Bing, Dogpile, etc. to gather target organization’s information such as employee details, login pages, intranet portals, etc. that helps in performing social engineering and other types of advanced system attacks.
- Perform Google hacking using tools such as GHDB, MetaGoofil, SiteDigger, etc.
- Gather target organization employees information from their personal profiles on social networking sites such as Facebook, LinkedIn, Twitter, Google+, Pinterest, etc. that assist to perform social engineering.
- Perform website footprinting using tools such as HTTrack Web Site copier, BlackWidow, Webripper, etc. to build a detailed map of website’s structure and architecture.
- Perform email footprinting using tools such as eMailTrackerPro, PoliteMail, Email Lookup-Free Email Tracker, etc. to gather information about the physical location of an individual to perform social engineering that in turn may help in mapping target organization’s network.
- Gather competitive intelligence using tools such as Hoovers, LexisNexis, Business Wire, etc.
- Perform WHOIS footprinting using tools such as SmartWhois, Domain Dossier, etc. to create detailed map of organizational network, to gather personal information that assists to perform social engineering, and to gather other internal network details, etc.
- Perform DNS footprinting using tools such as DNSstuff, DNS Records, etc. to determine key hosts in the network and perform social engineering attacks.
- Perform network footprinting using tool such as Path Analyzer Pro, VisualRoute, Network Pinger, etc. to create a map of the target’s network.
- Implement social engineering techniques such as eavesdropping, shoulder surfing, and dumpster diving that may help to gather more critical information about the target organization.
- At the end of pen testing document all the findings.
Footprinting Pen Testing Report Templates
- Information obtained through:
- search engines
- people search
- social networking sites
- website footprinting
- email footprinting
- competitive intelligence
- WHOIS footprinting
- DNS footprinting
- network footprinting
- social engineering
Module Summary
- Footprinting is the process of collecting as much information as possible about a target network, for identifying various ways to intrude into an organization’s network system.
- It reduces attacker’s focus area to specific range of IP address, network, domain name, remote access, etc.
- Attackers use search engines to extract information about a target.
- Attacker use social engineering tricks to gather sensitive information from social networking websites such as Facebook, MySpace, LinkedIn, Twitter, Pinterest, Google+, etc.
- Information obtained from target’s website enables an attacker to build a detailed map of website’s structure and architecture.
- Competitive intelligence is the process of identifying, gathering, analyzing, verifying, and using information about your competitors from resources such as the Internet.
- DNS records provide important information about location and type of servers.
- Attackers conduct traceroute to extract information about: network topology, trusted routers, and firewall locations.