Gyroscope adalah alat sensor yang dipakai untuk melacak rotasi atau perputaran suatu perangkat berdasarkan gerakan. Dengan kata lain gyroscope juga disebut sebagai perangkat yang dipakai untuk mempertahankan orientasi dari sebuah sudut agar tetap stabil.
Saat ini gyroscope banyak digunakan terutama pada smartphone sehingga kita bisa mengatur orientasi layar, bermain game, dll.
Output yang dihasilkan gyroscope berupa kecepatan sudut dari arah 3 sumbu yaitu sumbu x yang menjadi sudut phi (kanan dan kiri) , sumbu y yang nantinya akan menjadi sudut theta (atas bawah) dan sumbu z yang menjadi sudut psi (depan dan belakang).
Gyroscope yang digunakan pada mikrokontroler umunya alah gyroscope MEMS (Micro Elecromagnetic System) yang berukuran kecil. Sensor giroskop di dalam MEMS berukuran kecil (antara 1 hingga 100 mikrometer, seukuran rambut manusia). Ketika gyro diputar, sebuah massa beresonansi kecil akan digeser saat terjadi perubahan kecepatan sudut. Gerakan ini diubah menjadi sinyal listrik berarus sangat rendah yang mana dapat diperkuat dan dibaca oleh mikrokontroler.
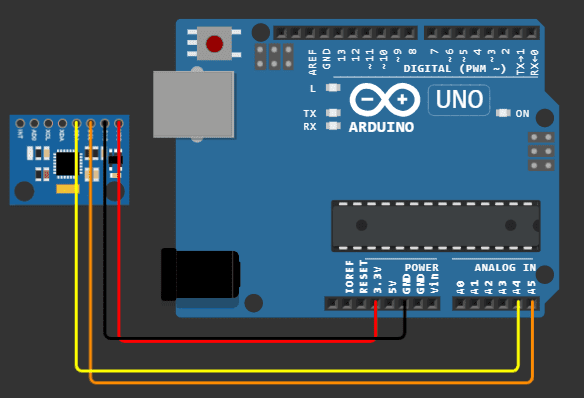
Rangkaian Gyroscope
Kode Program
#include <Adafruit_MPU6050.h>
#include <Adafruit_Sensor.h>
#include <Wire.h>
Adafruit_MPU6050 mpu;
void setup(void) {
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial)
delay(10); // will pause Zero, Leonardo, etc until serial console opens
Serial.println("Adafruit MPU6050 test!");
// Try to initialize!
if (!mpu.begin()) {
Serial.println("Failed to find MPU6050 chip");
while (1) {
delay(10);
}
}
Serial.println("MPU6050 Found!");
mpu.setAccelerometerRange(MPU6050_RANGE_8_G);
Serial.print("Accelerometer range set to: ");
switch (mpu.getAccelerometerRange()) {
case MPU6050_RANGE_2_G:
Serial.println("+-2G");
break;
case MPU6050_RANGE_4_G:
Serial.println("+-4G");
break;
case MPU6050_RANGE_8_G:
Serial.println("+-8G");
break;
case MPU6050_RANGE_16_G:
Serial.println("+-16G");
break;
}
mpu.setGyroRange(MPU6050_RANGE_2000_DEG);
Serial.print("Gyro range set to: ");
switch (mpu.getGyroRange()) {
case MPU6050_RANGE_250_DEG:
Serial.println("+- 250 deg/s");
break;
case MPU6050_RANGE_500_DEG:
Serial.println("+- 500 deg/s");
break;
case MPU6050_RANGE_1000_DEG:
Serial.println("+- 1000 deg/s");
break;
case MPU6050_RANGE_2000_DEG:
Serial.println("+- 2000 deg/s");
break;
}
mpu.setFilterBandwidth(MPU6050_BAND_21_HZ);
Serial.print("Filter bandwidth set to: ");
switch (mpu.getFilterBandwidth()) {
case MPU6050_BAND_260_HZ:
Serial.println("260 Hz");
break;
case MPU6050_BAND_184_HZ:
Serial.println("184 Hz");
break;
case MPU6050_BAND_94_HZ:
Serial.println("94 Hz");
break;
case MPU6050_BAND_44_HZ:
Serial.println("44 Hz");
break;
case MPU6050_BAND_21_HZ:
Serial.println("21 Hz");
break;
case MPU6050_BAND_10_HZ:
Serial.println("10 Hz");
break;
case MPU6050_BAND_5_HZ:
Serial.println("5 Hz");
break;
}
Serial.println("");
delay(100);
}
void loop() {
/* Get new sensor events with the readings */
sensors_event_t a, g, temp;
mpu.getEvent(&a, &g, &temp);
/* Print out the values */
Serial.print("Acceleration X: ");
Serial.print(a.acceleration.x);
Serial.print(", Y: ");
Serial.print(a.acceleration.y);
Serial.print(", Z: ");
Serial.print(a.acceleration.z);
Serial.println(" m/s^2");
Serial.print("Rotation X: ");
Serial.print(g.gyro.x);
Serial.print(", Y: ");
Serial.print(g.gyro.y);
Serial.print(", Z: ");
Serial.print(g.gyro.z);
Serial.println(" rad/s");
Serial.print("Temperature: ");
Serial.print(temp.temperature);
Serial.println(" degC");
Serial.println("");
delay(500);
}Penambahan Library
Tambahkan “Adafruit MPU6050”
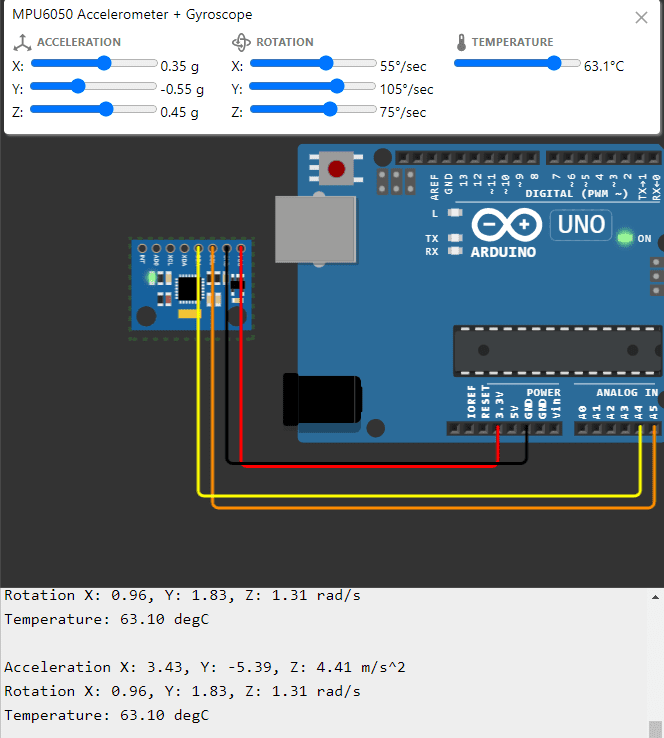
Jalankan Program
- Klik Sensor MPU 6050, dan atur sumbu X, Y, dan Z untuk melakukan simulasi gerakan pad sensor.
- Akan muncul tulisan pada serial monitor yang menunjukkan perubahan nilai setelah sumbu diubah.
- Klik Stop Simulation untuk menghentikan simulasi.
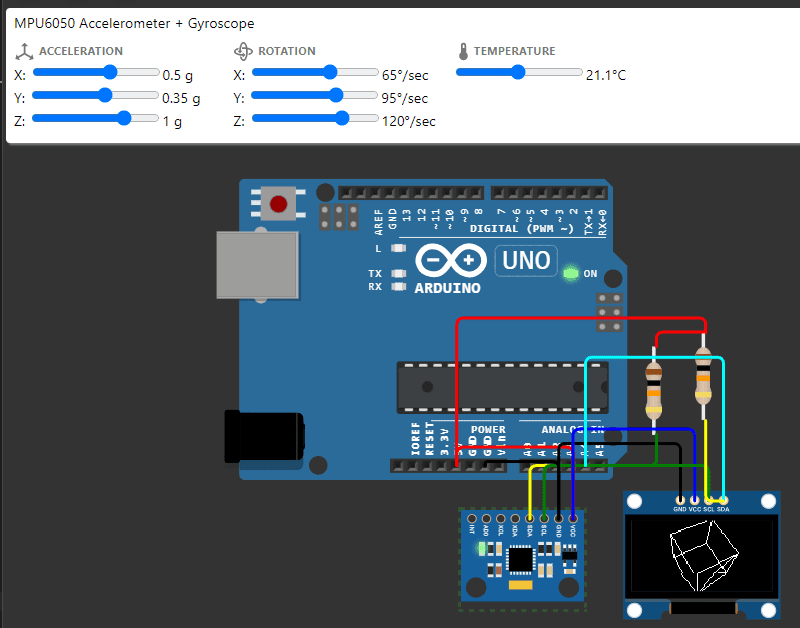
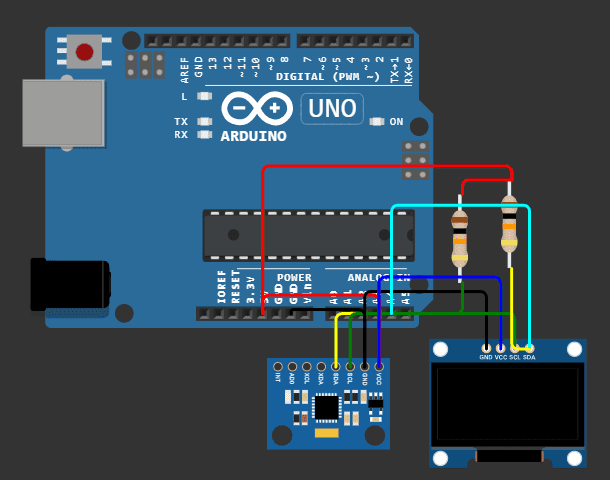
Sensor Gyroscope dengan OLED
Rangkaian Gyroscope dengan OLED
Kode Program
#include <Wire.h>
#include <Adafruit_SSD1306.h>
#include <Adafruit_GFX.h>
#include <Adafruit_NeoPixel.h>
Adafruit_SSD1306 display( 128, 64); // 128 pixels width, 64 pixels height
#define LED_PIN 6
#define LED_COUNT 1
Adafruit_NeoPixel neoPixel( LED_COUNT, LED_PIN, NEO_GRB + NEO_KHZ800);
const int mpuAddress = 0x68; // I2C address of the MPU-6050
float xByGyro, yByGyro, zByGyro; // Global variables for the rotation by gyro
// Set the origin in the middle of the display
const int xOrigin = 64;
const int yOrigin = 32;
const float viewDistance = 150.0; // higher for less perspective, lower for more.
// Vertices for a cube
// A cube has 8 corners and each coordinate has x,y,z values.
#define NUM_VERTICES 8
const int cube_vertex[NUM_VERTICES][3] =
{
{ -20, -20, 20 }, // x, y, z
{ 20, -20, 20 },
{ 20, 20, 20 },
{ -20, 20, 20 },
{ -20, -20, -20 },
{ 20, -20, -20 },
{ 20, 20, -20 },
{ -20, 20, -20 }
};
// The wirefram is to display the lines on the OLED display
// It contains the corners of the shape in 2D coordinates
int wireframe[NUM_VERTICES][2];
void setup()
{
Serial.begin( 115200);
Wire.begin();
// Initialize the OLED display and test if it is connected.
if( !display.begin( SSD1306_SWITCHCAPVCC, 0x3C))
{
Serial.println(F( "SSD1306 allocation failed"));
for(;;); // halt the sketch if error encountered
}
// Initialize the MPU-6050 and test if it is connected.
Wire.beginTransmission( mpuAddress);
Wire.write( 0x6B); // PWR_MGMT_1 register
Wire.write( 0); // set to zero (wakes up the MPU-6050)
auto error = Wire.endTransmission();
if( error != 0)
{
Serial.println(F( "Error, MPU-6050 not found"));
for(;;); // halt the sketch if error encountered
}
// Initialize the NeoPixel
neoPixel.begin();
}
void loop()
{
Wire.beginTransmission( mpuAddress);
Wire.write( 0x3B); // Starting with register 0x3B (ACCEL_XOUT_H)
Wire.endTransmission( false); // No stop condition for a repeated start
// The MPU-6050 has the values as signed 16-bit integers.
// There are 7 values in 14 registers.
int16_t AcX, AcY, AcZ, Tmp, GyX, GyY, GyZ;
Wire.requestFrom( mpuAddress, 14); // request a total of 14 bytes
AcX = Wire.read()<<8 | Wire.read(); // 0x3B (ACCEL_XOUT_H) & 0x3C (ACCEL_XOUT_L)
AcY = Wire.read()<<8 | Wire.read(); // 0x3D (ACCEL_YOUT_H) & 0x3E (ACCEL_YOUT_L)
AcZ = Wire.read()<<8 | Wire.read(); // 0x3F (ACCEL_ZOUT_H) & 0x40 (ACCEL_ZOUT_L)
Tmp = Wire.read()<<8 | Wire.read(); // 0x41 (TEMP_OUT_H) & 0x42 (TEMP_OUT_L)
GyX = Wire.read()<<8 | Wire.read(); // 0x43 (GYRO_XOUT_H) & 0x44 (GYRO_XOUT_L)
GyY = Wire.read()<<8 | Wire.read(); // 0x45 (GYRO_YOUT_H) & 0x46 (GYRO_YOUT_L)
GyZ = Wire.read()<<8 | Wire.read(); // 0x47 (GYRO_ZOUT_H) & 0x48 (GYRO_ZOUT_L)
// The acceleration is directly mapped into the angles.
// That is rather artificial.
// The combined gravity could be used for an angle, while ignoring the strength.
//
// The gyro sets the rotation speed.
// The angle created by the rotation speed is added to angle by the accelerometer.
//
// The conversion from the sensor values to the rotation is just a value
// that makes it look good on the display.
float xByAccel = (float) AcX * 0.0001; // static angle by accelerometer
float yByAccel = (float) AcY * 0.0001;
float zByAccel = (float) AcZ * 0.0001;
xByGyro += (float) GyX * 0.00001; // moving angle by gyro
yByGyro += (float) GyY * 0.00001;
zByGyro += (float) GyZ * 0.00001;
float x = xByAccel + xByGyro; // combine both angles
float y = yByAccel + yByGyro;
float z = zByAccel + zByGyro;
// Keep the radians in range (although the cos/sin functions accept every value)
if( x < 0.0)
x += 2.0 * M_PI;
else if( x > 2.0 * M_PI)
x -= 2.0 * M_PI;
if( y < 0.0)
y += 2.0 * M_PI;
else if( y > 2.0 * M_PI)
y -= 2.0 * M_PI;
if( z < 0.0)
z += 2.0 * M_PI;
else if( z > 2.0 * M_PI)
z -= 2.0 * M_PI;
// Draw 3D picture
for (int i = 0; i < NUM_VERTICES; i++)
{
// Rotate Y
float rotx = cube_vertex[i][2] * sin(y) + cube_vertex[i][0] * cos(y);
float roty = cube_vertex[i][1];
float rotz = cube_vertex[i][2] * cos(y) - cube_vertex[i][0] * sin(y);
// Rotate X
float rotxx = rotx;
float rotyy = roty * cos(x) - rotz * sin(x);
float rotzz = roty * sin(x) + rotz * cos(x);
// Rotate Z
float rotxxx = rotxx * cos(z) - rotyy * sin(z);
float rotyyy = rotxx * sin(z) + rotyy * cos(z);
float rotzzz = rotzz;
// Add depth perspective
rotxxx *= viewDistance / (viewDistance + rotzzz);
rotyyy *= viewDistance / (viewDistance + rotzzz);
// Bring to middle of screen
rotxxx += (float) xOrigin;
rotyyy += (float) yOrigin;
// Store new vertices values for wireframe drawing
wireframe[i][0] = (int) rotxxx;
wireframe[i][1] = (int) rotyyy;
wireframe[i][2] = (int) rotzzz;
}
draw_wireframe();
// Set the color of the NeoPixel according to the temperature
// Temperature by the MPU-6050 is -40 to 85.
// According to the datasheet:
// Temperature in Celsius = (raw_value / 340) + 36.53
// The Hue range for the NeoPixel is the full uint16_t range.
float Celsius = ((float) Tmp / 340.00) + 36.53;
float hue = (Celsius + 40.0) / 125.0 * 65535.0;
uint32_t rgbcolor = neoPixel.ColorHSV( (uint16_t) hue);
neoPixel.setPixelColor( 0, rgbcolor);
neoPixel.show(); // update new values to NeoPixel
}
void draw_wireframe(void)
{
// Start with a empty buffer
display.clearDisplay();
// A cube has 8 points and 12 sides.
// The wireframe contains the 8 points, and the 12 lines are drawn here.
display.drawLine( wireframe[0][0], wireframe[0][1], wireframe[1][0], wireframe[1][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[1][0], wireframe[1][1], wireframe[2][0], wireframe[2][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[2][0], wireframe[2][1], wireframe[3][0], wireframe[3][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[3][0], wireframe[3][1], wireframe[0][0], wireframe[0][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[4][0], wireframe[4][1], wireframe[5][0], wireframe[5][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[5][0], wireframe[5][1], wireframe[6][0], wireframe[6][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[6][0], wireframe[6][1], wireframe[7][0], wireframe[7][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[7][0], wireframe[7][1], wireframe[4][0], wireframe[4][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[0][0], wireframe[0][1], wireframe[4][0], wireframe[4][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[1][0], wireframe[1][1], wireframe[5][0], wireframe[5][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[2][0], wireframe[2][1], wireframe[6][0], wireframe[6][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[3][0], wireframe[3][1], wireframe[7][0], wireframe[7][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
// Extra cross face on one side
display.drawLine( wireframe[1][0], wireframe[1][1], wireframe[3][0], wireframe[3][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
display.drawLine( wireframe[0][0], wireframe[0][1], wireframe[2][0], wireframe[2][1], SSD1306_WHITE);
// Write the new picture to the display
display.display();
}Penambahan Library
Tambahkan Adafruit MPU 6050.
Tambahkan Adafruit SSD1306.
Tambahkan Adafruit GFX Library
Jalankan Program
Program tersebut digunakan untuk menampilkan posisi gyroscope dengan visualisasi pada OLED.
- Klik Sensor MPU6050, dan atur nilai X, Y, dan Z sesuai dengan keinginan.
- OLED akan menampilkan gambar kubus sesuai dengan orientasi yang diatur pada sensor MPU 6050.